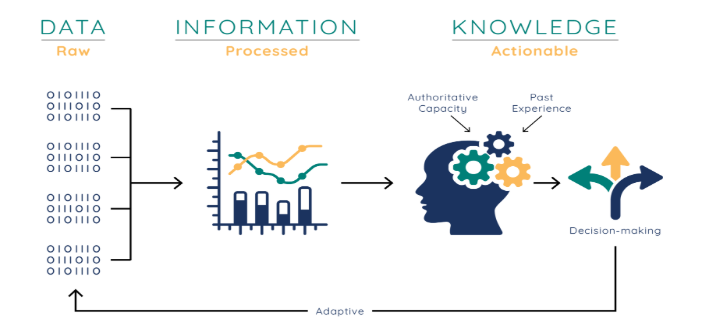
Data, Information, and Knowledge
DATA
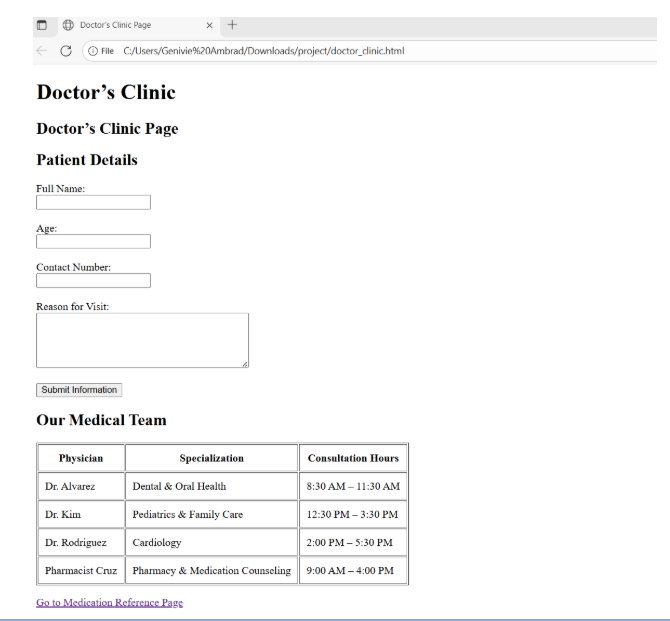
Data is raw, unprocessed facts and figures. It's like the building blocks of information. Think of it as individual pieces of a puzzle, each holding a small part of the bigger picture. By itself, a single piece of data doesn't convey much meaning.
INFORMATION
Information is data that has been processed, organized, and interpreted to give it meaning and context. It's like transforming raw ingredients into a delicious meal. While data is the raw material, information is the cooked dish, ready to be consumed and understood.
KNOWLEDGE
Knowledge is the application of information and experience to understand and solve problems. It's the ability to interpret information, recognize patterns, and draw meaningful conclusions. Think of it as the wisdom gained from learning and practice.
Data is a collection of facts, numbers, or other information that can be used to analyze or make decisions. It is generally raw information that simply includes basic numbers or texts. Information is the data that has been organized and analyzed to be useful for decision making. And knowledge is the understanding, awareness, or familiarity gained through experience, education, or learning.
The transformation begins with data collection - gathering raw facts from various sources like databases, sensors, or surveys. Next, data processing cleans and organizes this raw data, removing errors and inconsistencies. The processed data is then analyzed to identify patterns and trends, generating meaningful information presented through reports or visualizations. Finally, this information is interpreted within context, combined with experience and expertise, to create knowledge that enables informed decision-making and problem-solving.
Weather Forecasting:
• Data: Temperature readings, humidity levels, wind speed, atmospheric pressure, satellite images.
• Information: A cold front is moving in, bringing cooler temperatures and potential rain showers.
• Knowledge: Based on historical patterns, the meteorologist predicts a 70% chance of rain tomorrow.
Planning a Vacation:
• Data: A list of potential destinations (Paris, Rome, Tokyo, Bali), Budget: $3,000.
• Information: Researching flight costs, identifying tourist attractions, checking weather forecasts.
• Knowledge: Realizing that Paris aligns best with budget and interests, identifying affordable yet highly-rated accommodations.